Docker is a hugely popular containerization platform that enables developers to build and deploy applications inside containers. Containers are isolated environments that package an entire application alongside its dependencies, libraries, configuration files, and everything required to make it run regardless of the computing environment.
In this guide, we focus on how to install Docker on Ubuntu 22.04.
Step 1: Update the system
The first step is to refresh the repositories. To do so, run the command:
$ sudo apt update
Step 2: Install dependencies
Some dependencies are needed for the installation to go along seamlessly. Therefore, run the following command to install them:
$ sudo apt install apt-transport-https curl gnupg-agent ca-certificates software-properties-common -y
Once the dependencies have been installed, proceed to the next step.
Step 3: Install Docker on Ubuntu 22.04
With the requirements installed, the next step is to install Docker. We will install the Docker Community Edition ( Docker CE ) which is opensource and free to download and use.
To do so, we will add the GPGK key
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Once added, add the Docker repository as follows.
NOTE:
Since Ubuntu 22.04 is yet to be officially released, add the repository for Ubuntu 20.04 Stable.
$ sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal stable"
With the GPG key and the repository added, run the following command to install Docker and associated packages.
$ sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y
This installs Docker and all the additional packages, libraries, and dependencies required by Docker and associated packages.
Once the command runs successfully, consider adding the currently logged-in user to the docker group. This allows you to run docker without invoking sudo.
$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
$ newgrp docker
You can now run Docker commands as a regular user without any challenges.
Step 4: Confirm that Docker is installed
To verify that Docker is installed, run the command:
$ docker version
From the output, you can see that we have installed Docker 20.10 which is the latest version of Docker at the time of publishing this guide.

Step 5: Manage Docker Service
By default, Docker autostarts upon installation. To verify this, run the command:
$ sudo systemctl status docker
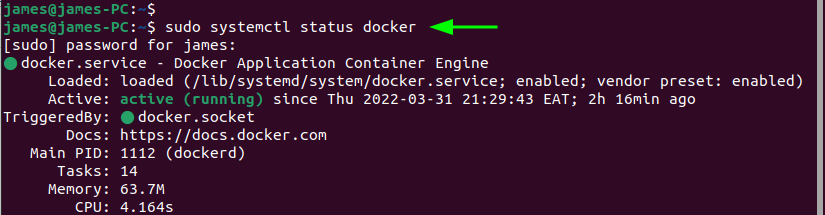
If, for any reason, Docker is not running, simply execute the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start docker
To enable Docker to start automatically every time on system startup, run the command:
$ sudo systemctl enable docker
To restart Docker run:
$ sudo systemctl restart docker
Step 5: Test Docker
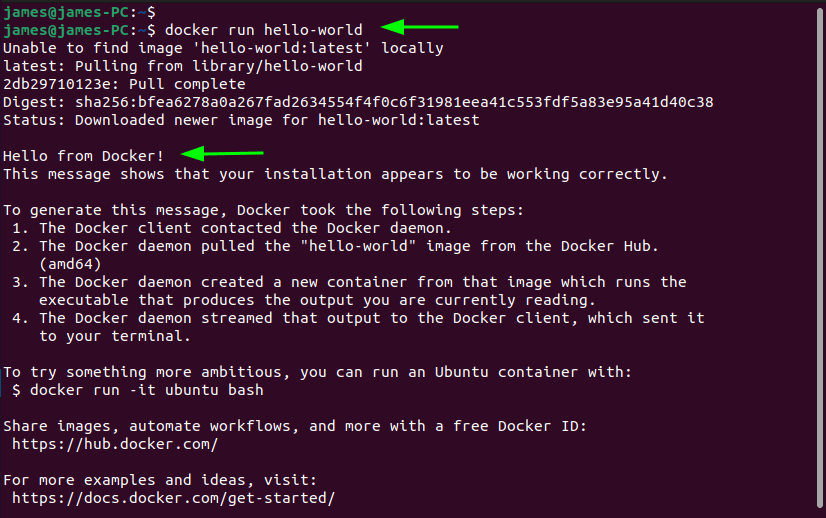
To give Docker a test run, we will pull a ‘hello-world’ image from Docker Hub. From the image, a container will be created that displays a ‘Hello world’ message on the terminal along with the steps of what just happened after the command was executed.
So, we will run the command:
$ docker run hello-world
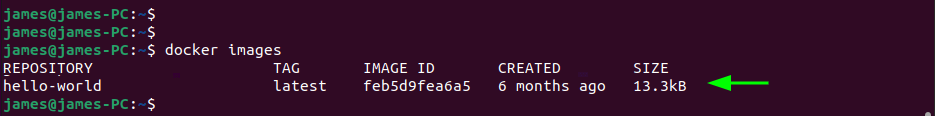
To confirm the images on the system, run the command:
$ docker images
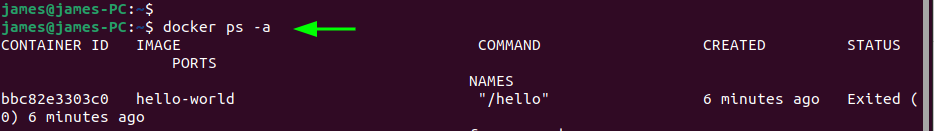
 After the container is created, it exits or stops automatically. You can still check stopped containers as shown.
After the container is created, it exits or stops automatically. You can still check stopped containers as shown.
$ docker ps -a
Conclusion
And this wraps up our guide. In this guide, we walked you through the installation of Docker on Ubuntu 22.04.

