Keeping your CPU temperature at an optimum level is crucial for the smooth running of your system. Overheating can be detrimental to your PC and If not kept in check, it can damage other motherboard components. Modern PCs usually have a sound cooling system that keeps the temperature in check and prevents overheating. The same cannot be said of older systems whose cooling systems may not be as efficient. In addition, elevated temperatures can be due to blocked ventilation vents and sometimes running multiple applications with high power consumption. In this guide, we will explore various ways that you can employ to check the CPU temperature on Ubuntu.
How to check the CPU temperature on Ubuntu systems
There are two ways that you can use to check your CPU temperature: Using the lm_sensors tool or the Psensor graphical tool. Let’s explore each of these tools:
Method 1. Using the lm_sensors tool
The lm_sensors tool is a command-line utility used to keep a watch on your CPU core and hard disk drive temperature. Incase Lm_Sensors command is not installed in your distribution, use the distributions package manager to install the Lm_Sensors package on your Linux PC.
Installation of Lm_Sensors
You can install the lm_sensors program on various Linux distributions as shown:
On Ubuntu / Debian
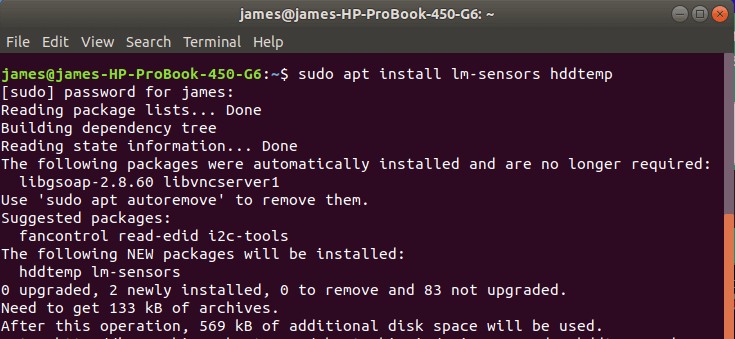
Lm sensors program is installed on Ubuntu using the apt package manager as shown:
$ sudo apt install lm-sensors hddtemp
On Arch / Manjaro
For Arch distros use the Pacman package manager to install as shown in the command below;
$ sudo pacman -S lm-sensors
On CentOS / RHEL & Fedora
For RedHat distributions such as CentOS & Fedora, use the dnf package manager to install the lm_Sensors tool.
$ sudo dnf install lm-sensors
Configuration of Lm_Sensors
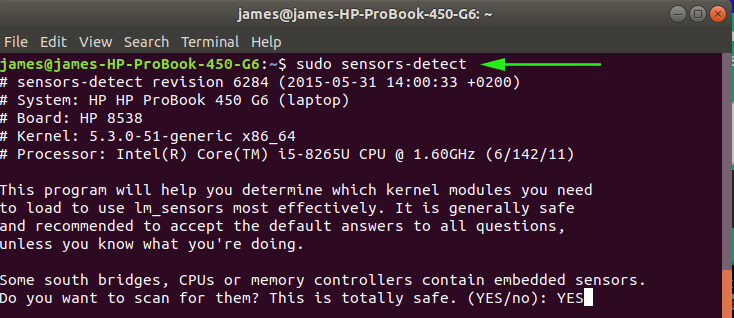
After the installation of the lm_sensors package, some configuration is required to ensure that the application can gather temperature readings from the CPU cores on your PC. To achieve this, run the sensors-detect command with sudo privileges if you are running as a regular user as shown to begin the configuration;
$ sudo sensors-detect
The program will begin to scan your processor and memory modules.
The configuration process begins with a couple of questions. You will be presented with the first question: “Some south bridges, CPUs or memory controllers contain embedded sensors. Do you want to scan for them? This is totally safe”. Type out “Yes” in the prompt to begin.
After selecting “YES,” the second question states, “Some Super I/O contain embedded sensors. We have to write to standard I/O ports to probe them. This is usually safe. Do you want to scan for Super I/O sensors?” Just like the first question, choose “Yes” to allow Lm_Sensors to scan.
Several other questions will follow upon which you will answer “Yes”. This will take a couple of minutes as the program continues probing your hardware components.
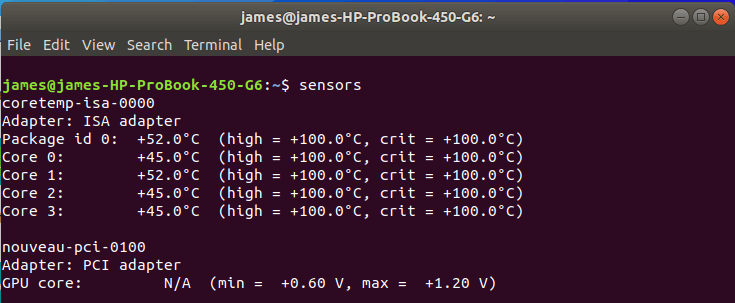
When the configuration is done, check the CPU temperature by invoking the sensors command. This will display the temperature of your CPU cores as shown below.
$ sensors
Method 2. Using the Psensors tool
Psensor is a graphical tool that relies on the lm_sensors program to display temperature readings in a graphical format. So ensure that you have installed lm_sensors first. Once you have installed lm_sensors install the Psensor application using the command:
$ sudo apt install psensor
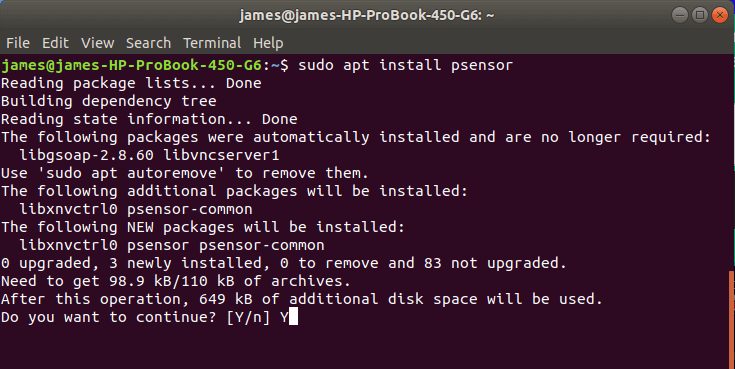
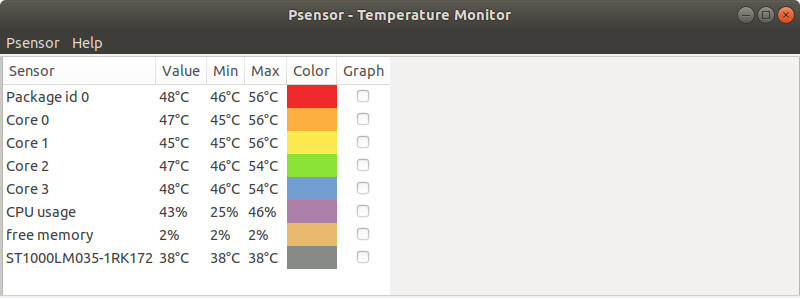
Once the installation is complete, you can use the application to search for the Psensor application and launch it. Therefore, the window below will be displayed:
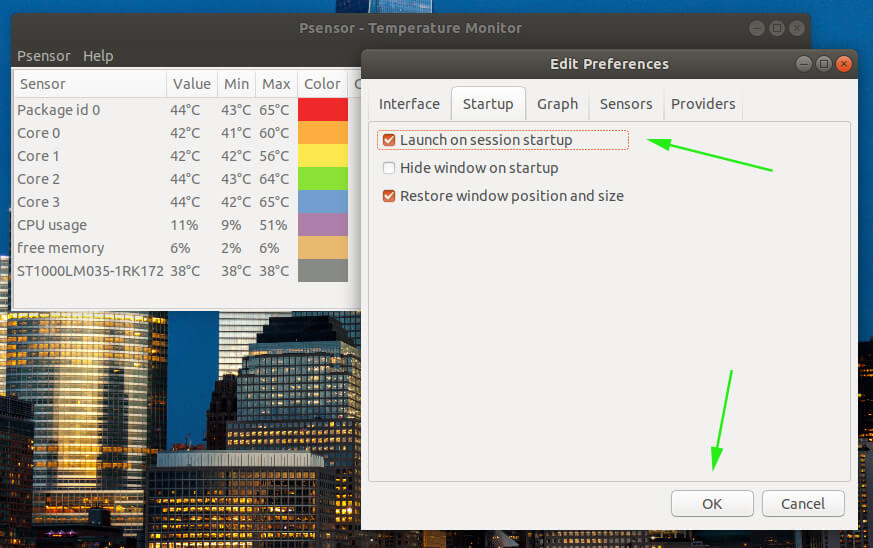
To pin the application on the top bar, click on ‘Psensor‘ and click on ‘Startup‘. Next click on the “launch session startup” option.
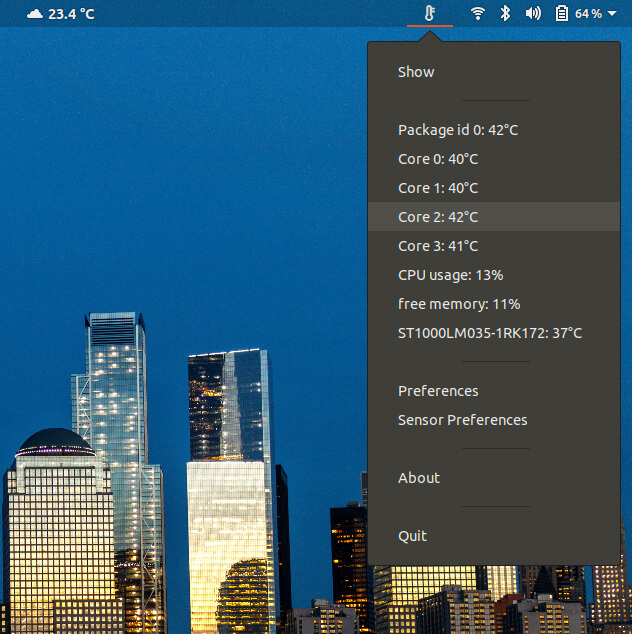
And this is what you get. You can click on the thermometer symbol to keep tabs on the temperature readings of your CPU cores and hard drive.
NOTE:
Unfortunately, Checking CPU temperature doesn’t work on virtualized instances such as a VPS or managed cloud server since the CPU and other hardware resources are virtualized.
This brings us to the end of this topic. We have covered two applications that help users monitor temperature readings of the CPU cores. This ensures that the CPU doesn’t overheat and lead to the malfunction of your system. We hope this article was informative. Give it a try and feel welcome to give us your feedback. Thank you.

