Hundreds of Linux distributions abound, each with its own features and look and feel. Some of the commonly used Linux distributions include Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, RedHat, ArchLinux and OpenSuse. Knowing how to check the version of Linux you are using pays comes in handy in order to know which package manager to use and which software packages need to be installed. In this guide, you will learn how to check Linux version of the OS that you are working on.
How to check your Linux version
There are 2 primary ways that you can use to check your Linux version of the distribution you are working on:
- Command-line
- Graphical
Let’s take a look at each in turn. For this guide, you will need to have a running Linux system. If you don’t have one, you can easily deploy a Managed cloud server for only $3.71 per month.
1) Check Linux version on the command line
For the terminal geeks or those who prefer working away on the terminal, you can check your Linux’s version
a) Using the lsb_release command
To check the Linux version you are using issue the lsb_release command as shown
$ lsb_release -a
Sample Output
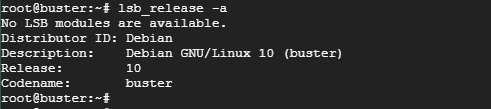
The command displays information such as the Distributor ID, description number, the release, and codename. We can clearly see from the output that we are running Debian 10 Linux also referred to as Buster.
To get the description only, use the -d option as shown
$ lsb_release -d
Sample Output
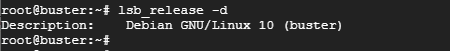
b) Using the os_release command
Another command-line utility you can use is the os_release command option as shown
$ cat /etc/os-release
Sample Output
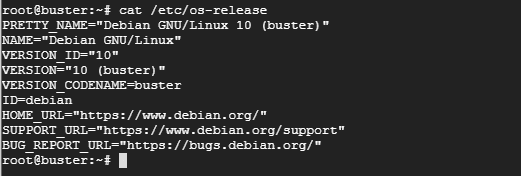
c) Using the /etc/issue command
The /etc/issue file is a file that contains the system’s identification information that is displayed just before a login prompt. To check information about the Linux version you are using, run the command:
$ cat /etc/issue
Sample Output
![]()
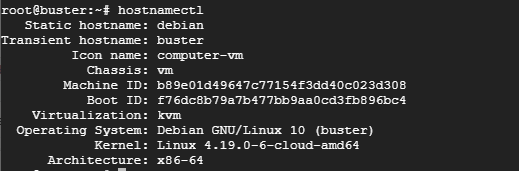
d) Using hostnamectl command
The hostnamectl command is a utility that comes with systemd systems. It’s used for changing the system’s hostname and prints a great deal of information such as static hostname, chassis Type, machine ID, Boot ID, Operating System, and kernel to mention a few.
# hostnamectl
Sample Output
2) Check Linux version using graphical means
If working on the terminal is not your fantasy, then a few graphical options are available.
a) Neofetch
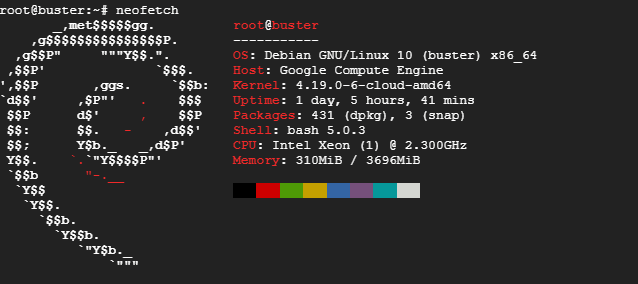
Neofetch is a handy and awesome bash script designed for Unix and Linux systems. It prints a spectrum of information such as operating system, CPU, Kernel version, architecture, and system uptime.
To install Neofetch on Debian/Ubuntu run
# sudo apt install neofetch
Sample Output

To run neofetch simply run
# neofetch
Sample Output
For CentOS / RHEL follow the steps below
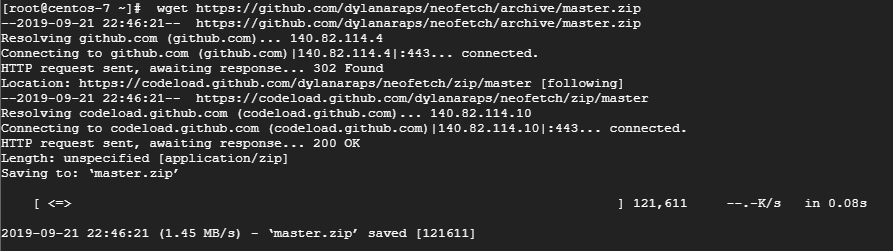
Step 1: Download the Neofetch zipped file as shown
$ wget https://github.com/dylanaraps/neofetch/archive/master.zip
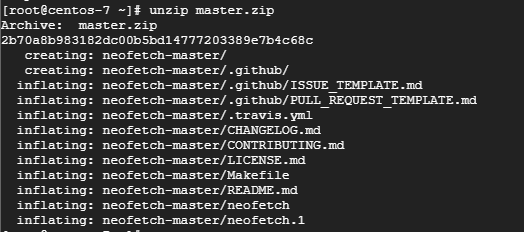
Step 2: Unzip the zipped file
# unzip master.zip
Step 3: Navigate to the Neofetch directory
# cd neofetch-master
![]()
Step 3: Run the command below
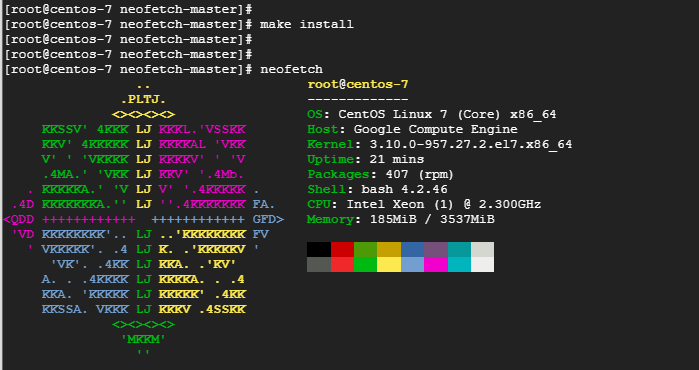
# make install
Step 4: Finally, to launch Neofetch run
# neofetch
Wrapping now
It’s our hope that you found this tutorial insightful and educative. We are confident that you can now verify your Linux version without much of a hassle. Your feedback is most welcome.

